Code Element
The code element is used to apply Javascript to the skin.
The code element is used to add custom JavaScript and CSS to your skin. When you add scripts with custom properties, those properties appear as parameters in the interface. The code element itself can also be saved as a reusable component.
Code Element Custom Properties
User-definable parameters added to JavaScript will appear here as interactive settings. These are available only when JavaScript is selected in the Code Element properties.
Code Element
Type
Choose whether to add JavaScript code or CSS. When JavaScript is selected, Code Element Custom Properties will be available.
Code
JavaScript
Select this option to add JavaScript, custom properties, and CSS.
Use the text field to add JavaScript. If you need more space, use the Open Editor button to open a larger editor.
External File
You can save your code as an external file. Once the code is saved, From file will be selected and the file path will be shown. To locate or change the file, right-click the path to open the context menu.
Once code is added as an external file, the editor becomes read-only.
Custom Properties
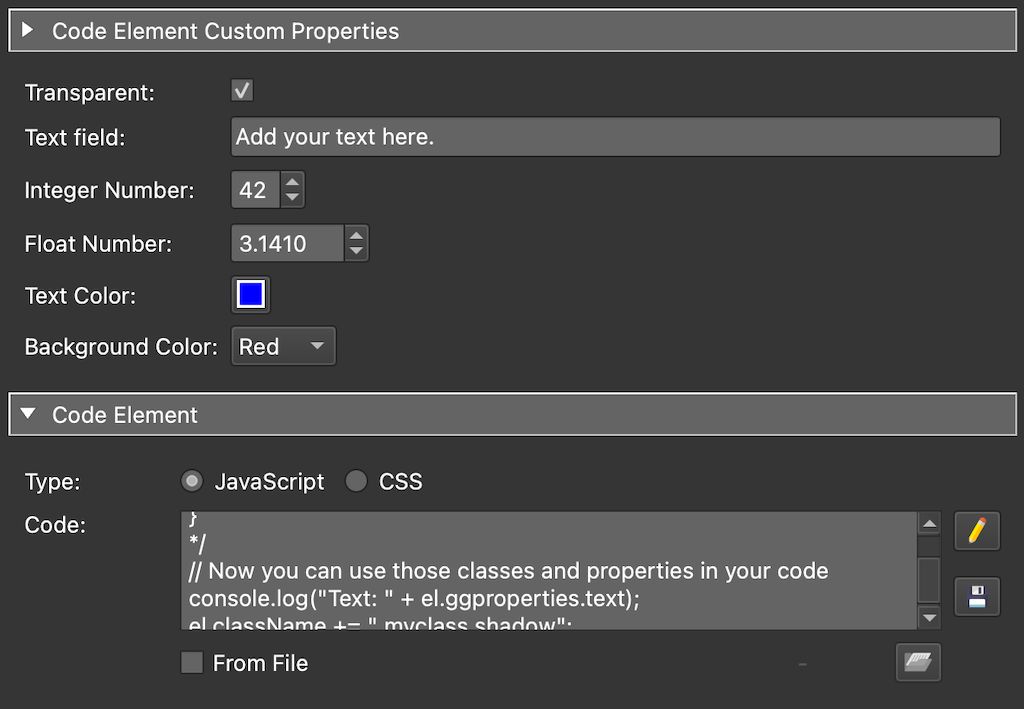
You can specify custom properties for the code element. These are defined in a JSON object called ggproperties. The example below shows how to define custom properties, what types are supported, and how to use their values in your JavaScript code.
If your code element uses skin variables and you copy it (to another skin) or save it as a component, you may want those variables to be included. To do this, specify the variables in a JSON object called ggvariables inside a special comment block that starts with /*! and ends with */.
In the example below, we specify that skin variables var1 and var2 should also be copied if the code element is copied or made into a component.
CSS
CSS can also be included inside the special comment block by wrapping it in a <style> tag. However, if you want to use the Code Element only for CSS, select CSS as the type.
Here is an example of such a comment block (plus some JavaScript code at the end) containing everything mentioned above. In practice, not everything has to be present. If none of this is needed, you can omit the comment block entirely:
/*! <style> .myclass { font-family: "Times", serif; line-height: 1.3; font-size: 20px; padding: 10px; } .glow { -webkit-filter: drop-shadow(0px 0px 3px rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5)); filter: drop-shadow(0px 0px 3px rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5)); } .shadow { -webkit-filter: drop-shadow(0px 0px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)); filter: drop-shadow(0px 0px 3px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)); } </style> { "ggproperties": [ { "id": "transparency", "type": "checkbox", "label": "Transparent", "default": true }, { "id": "text", "type": "text", "label": "Text field", "default": "Add your text here." }, { "id": "int_var", "type": "spinbox", "label": "Integer Number", "default": 42 }, { "id": "float_var", "type": "doublespinbox", "label": "Float Number", "default": 3.141 }, { "id": "color", "type": "color", "label": "Text Color", "default": "blue" }, { "id": "color2", "type": "combobox", "label": "Background Color", "default": "red", "values": [ { "label": "Black","value": "black" }, { "label": "Red", "value": "red" }, { "label": "Blue", "value": "blue" } ] } ], "ggvariables" : [ "var1", "var2" ] } */ // Now you can use those properties in your code console.log("Text: " + el.ggproperties.text); el.className += " myclass shadow"; el.style.color = el.ggproperties.color; el.style.background = el.ggproperties.color2; el.innerHTML = el.ggproperties.text; CSS
Select CSS if you simply want to use the Code Element to add just CSS.
External Files
External files are used for sharing JavaScript Code elements as Components. Any files that the element depends on will be included as part of the component and added to the skin when the component is used.
To add a file, click the plus button at the right of the row or double-click in the table. Choose whether the file should be a CSS or JavaScript file, then enter the URL.
Local Files
In the local files table, you can add files from your computer that will be included in the skin file and copied to the output folder when you export. For example, you might add font files to use in the CSS styles defined in the code element.
To add a file, click the plus button at the right of the row or double-click within the table. Navigate to the file. The file will appear in the table. You can edit the file name in the table by clicking it. This will be the file name used when it is copied to the output folder. You can also prepend a subfolder so the file will be copied to a subfolder in the output.
For example, you could add a font file from your computer, myFont.ttf. Then, edit the file name in the table to fonts/myFont.ttf. When you export, this file will be copied to the output folder, in a subfolder called fonts.
Position
ID
Give the element a unique ID or name. An ID is given automatically and will be numerically ordered when more than one are added. If an ID is already used by another element, a warning symbol will appear next to the input field.
Point Hotspot Templates will have a menu that shows all the default template IDs as well as any template IDs used in the project.
Position
The X and Y coordinates for the element.
An element’s position is relative to its parent and to its anchored position (the Canvas is the parent to top level elements).
For example, a video that is anchored and placed in the middle of the Canvas will have its anchor set to center and X and Y set to 0. So, if the element is anchored to the horizontal center, the X coordinate is measured from the center of the parent to the horizontal center of the element. Likewise, if an element is anchored right, the x-coordinate is measured from the right side of the parent to the right side of the element as indicated by the arrows.
0. This makes it easier to precisely position elements, especially on the edges of the player. For example, to keep an element positioned on the bottom center of the player and a certain distance from the edge, set the anchor to center bottom and set the Y value to 20 pixels and X to 0.X and Y:
-
Percentage – Unit to set the position of the element based on the player’s size/window.
-
Pixels – Unit to set the actual location of the element within the skin.
-
CSS – Select CSS as a unit to allow for changing units when a logic block has been added or to use calculations.
- Example: Set the x position unit to CSS. Enter,
100pxin the edit field. Add a logic block, choose a trigger and add20%for the size, effectively switching units.
- Example: Set the x position unit to CSS. Enter,
Anchor
Use this grid to “stick” the element to a section of the player window. See above, to learn how the Anchor influences Position.
Size
The Hotspot Template and Node Marker do not have a size parameter.
Adjust the element’s size (width and height) in pixels. Width and Height:
-
Percentage – Unit to set the size of the element based on the player’s size/window.
-
Pixels – Unit to sets the actual size of the element.
-
Lock Aspect Ratio – Click the link icon to lock the element’s size aspect ratio when resizing in the Canvas or changing size values in the properties panel. This button is reset to off when another element is selected.
-
CSS – Select CSS as a unit to allow for changing units when a logic block has been added or to use calculations.
- Example: Position an element 50 pixels from the top and then set the height to
calc(100% - 50px). The element will then always have the same distance of 50px from the top and will extend straight down to the bottom.
- Example: Position an element 50 pixels from the top and then set the height to
-
Reset Size – Available for Image, Button, and SVG elements. Click to return to the image’s original size.
-
Reset Size/2 – Available for Image, Button, and SVG elements. Use this when you want to add a PNG or JPG to your project but still want it looking sharp in Hi-DPI displays. For example, if the skin requires a 32px image, use a 64px image and then click, Reset Size/2. This will then make it 32px in the skin but will still have all the pixels for a high resolution display.
Appearance
Scaling
Scales the element along the x and y axes. Doubling the value on either axis, for instance, will double the size of the element. If a scaling modifier is enabled, this scaling setting is ignored.
Center
Use this grid to determine how the element scales. The default is set to the center so the element will scale in or out from its center. If you anchor the scaling to the upper left corner, for example, the scaling will center from this point.
Angle
Use this parameter to adjust the angle of the element. It will use the Center grid (above) as its axis. For example, if the center is chosen, it will rotate around its center. If the bottom left corner is selected, the button will rotate around that corner.
Visible
Select or deselect to keep the element visible or invisible. Visibility or invisibility can be changed and toggled with actions.
Alpha
The transparency of the element. A setting of 1.000 is opaque. Lowering this number will increase the elements’s transparency.
Cursor
Choose which cursor shows when the mouse rolls over the element.
Inherit – The element will inherit the cursor from its parent element. This is the default for all elements except Button and Seekbar.
Hand – The hand cursor will show. This is the deafult for Button and Seekbar elements. When selected, the cursor is not inherited from its parent element.
Default – Choose this option to force the browser’s default cursor (usually an arrow). When selected, the cursor is not inherited from its parent element.
Masking
Container and Rectangle elements only Select Enabled to activate masking. Masking means that child elements of the container or rectangle will be clipped at the container or rectangle’s boundaries.
Accessibility
Tab Index
To make skin elements controllable via keyboard, they have to be added to the tab order of the web page. A tab index of -1 (the default) excludes the element from the tab order. A tab index of 0 includes the element in the tab order. Browsers will highlight the active element by putting a rectangle around them. Once a skin element is the active element, indicated by the highlight, hit the Enter/Return key to trigger its click action.
ARIA Label, Description, Details
These are attributes or propterties that are used to define the element and support the Role.
Label – Defines or names the element.
Description – Provide a brief description of the element.
Details – Provide an extended, detailed description of the element.
ARIA Roles
ARIA Roles are used to define UI elements (button, loading bar, etc.). Choose from the list which best defines the element.
Hidden
Select to hide all ARIA attributes.
Advanced
Z-Index
Set the CSS z-index property. Use numbers to set the stacking order or leave the setting at Default. Default will use the stacking order set in the Tree.
This is used to ensure that elements are displayed in the correct stacking order especially when close or overlapping.
Use the Logic Block to change the Z-index value using variables, for example.
Permeable
Select to make sure the element does not accept mouse clicks. This is useful for when you want to include an element in the skin but don’t want it to hinder the ability to interact with the panorama. For example, you could add a vignette or logo or border that when clicked on, will allow interaction with the panoramas.
Hotspot Proxy ID
Enter the corresponding ID. The ID comes from the hotspot’s ID field in the hotspot properties. Hotspot proxies give you the ability to link skin elements to specific hotspots. This means that the element will receive the same mouse and touch events as the hotspot (mouse click, mouse double-click, mouse enter, and mouse leave). You can also add {} to use node ID as hotspot proxies. Learn more.
CSS Classes
Enter the CSS class names for the selected element. You can enter more than one class separated by spaces. If you need more space, click the Edit button to the right of the field for a larger text field. No dot . needed.
Logic Block available. Use the Additive Mode, to apply different classes to the element. Every condition will add a class (or multiple classes) to the default list of classes set in the CSS classes property of the element or stylesheet. Classes set in the property are not be replaced but rather added to.
CSS Styles
Enter the CSS style attributes for the selected element. You can enter more than one style separated by semi-colons. If you need more space, click the Edit button to the right of the field for a larger text field.
CSS Styles Inner Element
Enter CSS style attributes for the selected element’s inner element. (Some skin elements, like Image, Video and External Image, have an inner element nested inside the element’s main <div>.)
For example, an image element can have a border: border-radius: 20px; border: 5px solid red;. This can also be entered with a line break: border-radius: 20px; border: 5px solid red;
Keyboard Shortcut
Enter the preferred key to control the action defined to the element. For example, select the text field, hit the up key on the keyboard. Then add a Mouse Click action. The element, when clicked or when the up key is pressed, will perform the assigned action.
Exclude from Translation
Select this option to not include this element in the skin’s translation file.
Safe Area
Available for the Container Element.
Select Use Safe Area for Position and Size to keep child elements of the container inside the safe area of the device. This option makes sure that the elements are always 100% visible and the skin will automatically react to the device’s safe area.
Make sure Ignore Safe Area is not select in the HTML template settings in the Web Output.
Actions
Actions or a set of directions can be applied to any element added to the skin to create interactivity.
Double-click in the Actions area or click the plus sign to the right to open the Action Settings.
See Skin Actions, for details on all actions.
Modifiers
Adding modifiers allows you to make elements move, scale or rotate when the panorama is being panned, tilted, zoomed or loaded. A good example of a use of a modifier is for a loading bar that scales in relation to how much of the panorama has been loaded.
Double-click in the Modifiers area or hit the plus sign to the right to open the Modifier Settings.
See Skin Modifiers, for more details on all modifiers.
Notes
Use this section to add information about the element. This is especially useful if you have a component and want to explain the elements inside that component.
Notes will show up as tooltips in the Tree.
